The advent of 3D image segmentation is revolutionizing the field of dental diagnostics and surgery by providing high-precision analysis of dental images. This technology enables detailed visualization of complex dental structures, allowing for more accurate diagnoses and streamlined treatment planning. By offering a more comprehensive view than traditional 2D imaging, 3D segmentation enhances the ability …
The advent of 3D image segmentation is revolutionizing the field of dental diagnostics and surgery by providing high-precision analysis of dental images. This technology enables detailed visualization of complex dental structures, allowing for more accurate diagnoses and streamlined treatment planning. By offering a more comprehensive view than traditional 2D imaging, 3D segmentation enhances the ability of dental professionals to plan and execute procedures with greater precision.
1. What is 3D Image Segmentation?
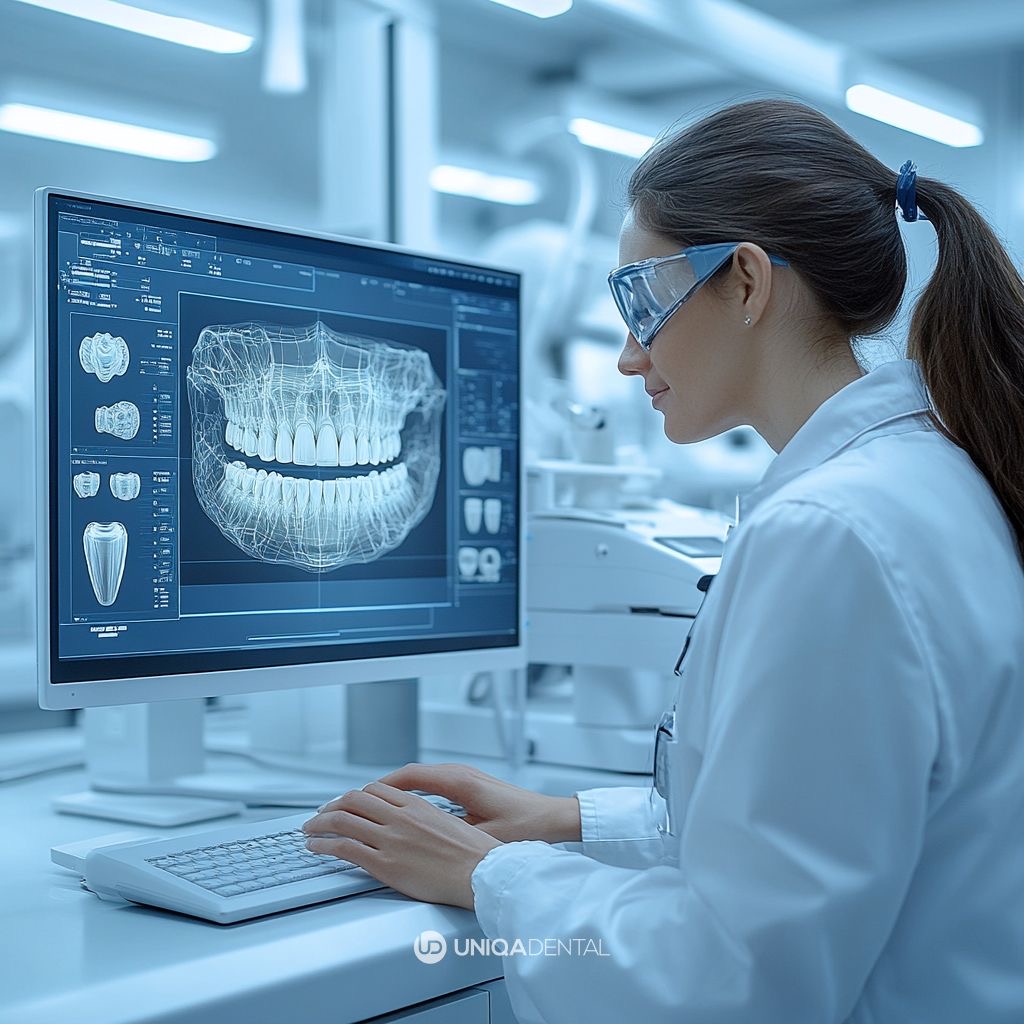
3D image segmentation is the process of partitioning a 3D image into distinct regions or components that correspond to various anatomical structures, such as teeth, bones, or nerves. In dentistry, it is primarily used for the detailed analysis of dental radiographs like CBCT (Cone Beam Computed Tomography) scans. By creating accurate, segmented images, dental professionals can isolate specific structures, such as the Inferior Alveolar Nerve (IAN), and better plan surgeries like implants or extractions.
Unlike traditional 2D imaging, which can only provide flat representations of structures, 3D segmentation gives dental professionals a three-dimensional view of the patient’s mouth, jawbone, and surrounding tissues. This added dimension of accuracy is critical for complex cases, such as orthodontics, maxillofacial surgery, or implant placement, where every millimeter counts.
2. Enhanced Diagnosis and Treatment Planning
One of the most significant advantages of 3D segmentation in dental diagnostics is its ability to provide highly accurate visual representations of a patient’s anatomy. For instance, when diagnosing periodontal disease or bone loss, 3D segmentation can detect even the smallest changes in bone density and structure, allowing for early interventions and better treatment outcomes. Additionally, it plays a vital role in mapping out nerves, blood vessels, and soft tissue, ensuring that these critical structures are avoided during surgery.
With more precise images, dental professionals can develop more accurate treatment plans. Whether it’s determining the ideal placement for dental implants or planning corrective jaw surgery, 3D segmentation helps practitioners identify the best course of action with a clear understanding of the patient’s unique anatomy. This reduces the risk of complications and improves the overall success rate of dental procedures.
3. Reducing the Risk of Nerve Damage
A common concern in dental surgeries, especially those involving implants or extractions, is the risk of damaging the Inferior Alveolar Nerve (IAN). 3D image segmentation plays a crucial role in minimizing this risk by providing a clear, detailed map of the nerve’s location. With this advanced visualization, dental surgeons can plan procedures in a way that ensures the nerve is protected, reducing the likelihood of post-operative complications such as numbness or pain.
For example, CoDental AI’s technology focuses on using 3D segmentation to accurately localize the IAN, enhancing safety during dental implant surgeries. By offering a precise and automated approach to segmenting the nerve, the technology ensures that dental professionals can operate with confidence and avoid critical mistakes that might affect patient outcomes.
4. Improving Surgical Efficiency
3D segmentation doesn’t just enhance diagnostic accuracy—it also improves the efficiency of dental surgeries. By providing detailed pre-operative planning, it reduces the need for intraoperative adjustments, enabling surgeons to perform procedures more quickly and accurately. This not only cuts down on surgery time but also leads to faster patient recovery.
For instance, during dental implant procedures, 3D segmentation allows for a virtual simulation of the surgery, giving the surgeon a clear roadmap to follow. This reduces the need for trial and error during the actual procedure and minimizes the chances of unforeseen complications. As a result, patients experience less time in the chair and quicker recovery times, while dental practices can improve workflow efficiency.
5. Future Applications and Developments
As 3D segmentation technology continues to advance, its applications in dental care are expected to grow even further. Emerging trends include integrating AI into 3D segmentation processes, allowing for real-time analysis and immediate diagnostic feedback. These AI-powered tools can analyze patient data more quickly than a human ever could, offering dental professionals critical insights in minutes rather than hours.
Looking ahead, the combination of 3D segmentation and AI has the potential to automate more aspects of dental diagnostics, leading to improved patient outcomes, reduced costs, and more streamlined care processes. As these technologies evolve, the future of dental care will undoubtedly become more efficient, accurate, and patient-centered.
Conclusion
3D image segmentation is a game-changing technology in dental diagnostics and surgery, offering unparalleled accuracy and detail in visualizing dental structures. By enabling precise diagnoses, reducing the risk of nerve damage, and improving surgical planning, 3D segmentation is reshaping how dental professionals approach treatment. As technology continues to advance, its role in transforming dental care will only grow, paving the way for more efficient, safer, and successful procedures.